Currency and Financial Instrument Correlation in FX Markets
Correlation—a statistical measure of how two variables move in relation to each other—plays a key role in shaping trading strategies, managing risk, and identifying market opportunities in FX. Correlation coefficients, which range from -1.0 to +1.0, help quantify the strength and direction of relationships between currency pairs. A value of +1.0 indicates perfect positive correlation, meaning the two variables move in the same direction 100% of the time. A coefficient of -1.0 reflects perfect negative correlation, where the variables move in opposite directions. For traders, understanding these nuances is crucial for crafting effective strategies. For example, a high positive correlation between EUR/USD and GBP/USD suggests that similar economic or geopolitical forces drive both pairs. This insight enables traders to anticipate movements and align their positions accordingly.
Currency correlation can reveal which pairs tend to move in tandem or opposition, while financial instrument correlation extends this analysis to commodities, indices, and cryptocurrencies. These relationships become even more significant during periods of geopolitical tension, economic uncertainty, or financial policy shifts.
Currency Correlation in FX Markets
Currency pairs are inherently connected, not only because they trade in pairs but due to broader economic and geopolitical factors. For example, when trading GBP/JPY, movements often reflect activity in the GBP/USD and USD/JPY pairs.
 Matthew Hunter, FX Derivatives and Trading at GPS Capital Markets, highlights a current trend in EUR/USD: “We’ve seen the single currency breach below 1.06 a couple of times. Once it does drop below the support level, there’s a wide consensus it will reach parity in the coming months.”
Matthew Hunter, FX Derivatives and Trading at GPS Capital Markets, highlights a current trend in EUR/USD: “We’ve seen the single currency breach below 1.06 a couple of times. Once it does drop below the support level, there’s a wide consensus it will reach parity in the coming months.”
This example shows how correlation analysis helps traders anticipate movements in interconnected pairs. As market participants watch the EUR/USD closely, its fluctuations underscore broader macroeconomic and geopolitical pressures. The recent breach below the 1.06 support level aligns with economic stressors across the Eurozone. Countries like Germany, grappling with potential recession, weigh heavily on the shared currency’s performance. Simultaneously, Spain’s economic growth highlights the challenges of maintaining a unified policy framework. These disparities within the Eurozone create uncertainty, making the EUR/USD pair an essential indicator for traders monitoring European economic health.
Positive correlation occurs when two pairs move in the same direction, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, often due to shared drivers like economic policy. Negative correlation, such as between EUR/USD and USD/CHF, indicates movement in opposite directions. These patterns allow traders to hedge positions or capitalize on predictable trends.
Financial Instrument Correlation: The Bitcoin Example
Financial instruments beyond currency pairs also exhibit correlations with FX markets. Bitcoin (XBTUSD), often viewed as a volatile and independent asset, presents unique opportunities and challenges for traders.
 Mark Allen, FX Trading & Derivatives at GPS Capital Markets, says: “USDCHF and USDJPY have a decent positive correlation of 0.660. They are the traditional global ‘safe-haven’ currencies, so I would expect them to move ‘in sync’ (Bye Bye Bye, ha!). I’m surprised that Bitcoin (XBTUSD) has a low correlation to any of the currencies. And a low correlation to gold (XAU). Bitcoin’s strongest correlation is vs. the AUDUSD at 0.195.”
Mark Allen, FX Trading & Derivatives at GPS Capital Markets, says: “USDCHF and USDJPY have a decent positive correlation of 0.660. They are the traditional global ‘safe-haven’ currencies, so I would expect them to move ‘in sync’ (Bye Bye Bye, ha!). I’m surprised that Bitcoin (XBTUSD) has a low correlation to any of the currencies. And a low correlation to gold (XAU). Bitcoin’s strongest correlation is vs. the AUDUSD at 0.195.”
Bitcoin’s current, modest positive correlation with the S&P500 (0.363) and its negligible relationship with other currencies or gold suggest its emerging role as a speculative asset rather than a traditional hedge. This evolving dynamic challenges the conventional belief that cryptocurrencies operate independently of broader market trends. For instance, Bitcoin’s correlation with AUD/USD reflects Australia’s increasing involvement in blockchain technology and digital asset adoption, hinting at regional influences. Bitcoin’s limited correlation with gold underscores its divergence from classic safe-haven behaviors, offering traders new considerations when building diversified portfolios.
This insight underscores Bitcoin’s evolving relationship with traditional markets, particularly its modest correlation with risk assets like equity indices. In a LinkedIn poll, we asked:
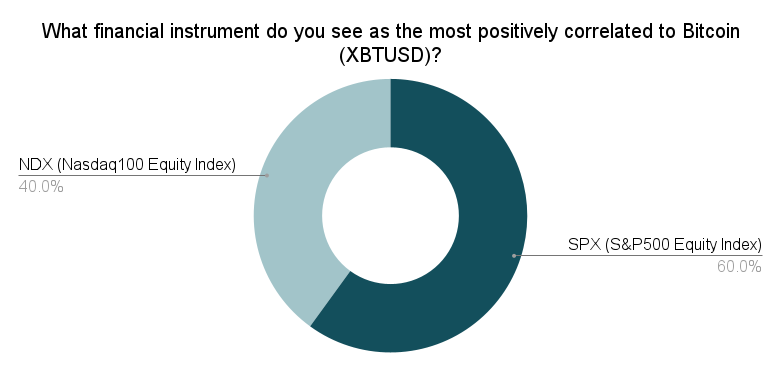
- SPX (S&P500 Equity Index): 60%
- NDX (Nasdaq100 Equity Index): 40%
- GBP/USD: 0%
- AUD/USD: 0%
Bitcoin’s divergence from traditional safe-haven assets like gold suggests its unique positioning in market portfolios.
The Role of Gold in Uncertain Times
Gold has long been a cornerstone of financial stability during geopolitical turmoil and economic uncertainty. On the brink of nuclear war or during other crises, gold’s value often increases as investors seek refuge from risk.
Gold’s inverse relationship with the US dollar highlights its role as a safe haven. When the dollar strengthens, gold prices typically decline, and vice versa. This interplay influences currency correlations, particularly in risk-off environments where assets like USD/JPY and USD/CHF also gain prominence.
Geopolitical Influences on Currency Correlation
Current events underscore the importance of understanding correlations. DXY is trading at 106.4, supported by safe-haven flows as tensions escalate between Russia and Ukraine. Meanwhile, EUR/USD has fluctuated within a narrow range, reflecting market uncertainty ahead of ECB President Lagarde’s remarks on financial stability.
These dynamics highlight the interconnectedness of economic indicators, monetary policies, and political developments in driving correlations. For instance, diverging interest rate paths between the US Federal Reserve and the European Central Bank create opportunities for traders leveraging EUR/USD and USD/CHF correlations.
Strategies for Leveraging Correlation
To effectively navigate correlation in FX markets, traders should:
- Hedge risks: Utilize negatively correlated pairs to mitigate losses. For example, pairing long EUR/USD with short USD/CHF positions can balance exposure.
- Diversify portfolios: Reduce risk by incorporating assets like equities or commodities, which exhibit different correlation patterns.
- Monitor economic data: Pay attention to macroeconomic indicators like CPI and interest rate decisions, which influence currency correlations over time.
Conclusion
Currency and financial instrument correlation offer critical insights for traders seeking to understand market dynamics and make informed decisions. Whether leveraging positively correlated pairs for consistent trends or using negative correlations for hedging, these tools are invaluable in today’s interconnected financial landscape.
During periods of uncertainty, assets like gold and currencies like USD/CHF gain prominence as safe havens, while unconventional instruments like Bitcoin continue to challenge traditional correlation models. By incorporating correlation analysis into their strategies, traders can navigate the complexities of global FX markets with greater confidence.
For businesses and institutions managing foreign exchange risks, GPS Capital Markets provides tailored tools and actionable advice. From hedging strategies to automated FX solutions like FXpert, GPS empowers clients to stay ahead in an ever-evolving market.

